Traffic potential determines how many visitors a keyword can realistically deliver to your site. Understanding this metric transforms your keyword research from volume-chasing to strategy building.
Most marketers focus solely on search volume. They target high-volume keywords and wonder why traffic never materialises.
The reality: search volume alone tells you almost nothing about actual traffic opportunity.
Traffic potential combines search demand with click-through behaviour, SERP features, ranking probability, and competitive dynamics. Targeted traffic consists of visitors who arrive with a specific goal aligned to your offer, and these users are more likely to convert than general visitors. This focused approach separates successful content strategies from wasted effort.
This guide shows you how to calculate traffic potential accurately, which tools deliver the most reliable estimates, and how to prioritise keywords based on realistic traffic forecasts rather than vanity metrics.
You’ll learn to identify keywords that appear low-volume but unlock substantial traffic through related queries, assess your genuine ranking probability, and build a traffic analysis framework that guides smarter content decisions.
Understanding Traffic Potential vs Search Volume
Search volume shows monthly searches for a specific keyword. Traffic potential reveals total visitors you can actually capture.
These metrics diverge significantly in practice.
A keyword with 5,000 monthly searches might deliver 200 visitors if you rank first. Another with 500 searches could bring 2,000 visitors if the top-ranking page captures dozens of related queries.
A single page can rank for dozens or hundreds of related queries. This multiplier effect makes traffic potential far more valuable than isolated search volume.
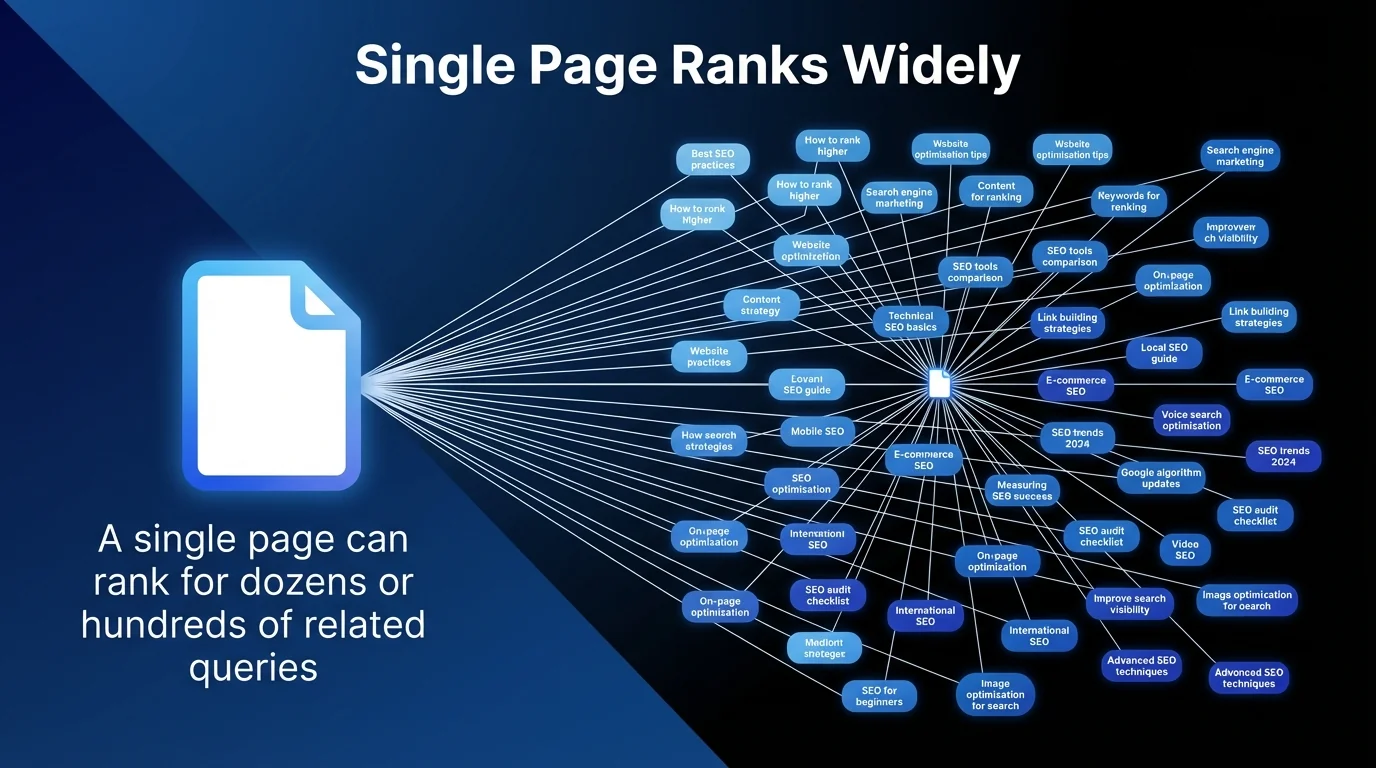
Consider a keyword like ’email marketing software’. It shows 10,000 monthly searches. But the top-ranking page also captures traffic from ‘best email tools’, ’email automation platforms’, ‘mailchimp alternatives’, and 200+ similar variations.
Total traffic potential? Over 50,000 monthly visitors from one strategic ranking.
Search volume measures a single query. Traffic potential measures the entire opportunity cluster around that query.
Why Search Volume Misleads
High search volume often correlates with zero-click searches. Users get answers directly in search results without visiting any site.
Informational queries like ‘what time is it in Tokyo’ generate massive search volume but zero traffic potential. Google answers the question in the SERP.
Commercial keywords face similar challenges. SERP features like shopping carousels, local packs, and featured snippets capture clicks before users reach organic results.
A keyword with 20,000 searches might only deliver 3,000 clicks across all organic positions combined.
The Traffic Potential Advantage
Traffic potential accounts for click-through rate variations by position and SERP layout. Around 25-30% of clicks for a typical query are captured by the top organic result. This percentage drops dramatically for positions two through ten.

Understanding these dynamics helps you forecast realistic traffic and prioritise keywords where you can actually rank competitively.
Traffic potential also reveals keyword difficulty context. A technically difficult keyword might still be achievable if competitors have weak content or limited domain authority.
Core Components of Traffic Potential Analysis
Calculating traffic potential requires four essential data points. Each component influences your final estimate.
Miss any element and your forecast becomes unreliable.
Search Volume and Variations
Start with primary keyword search volume. Then identify related queries, questions, and long-tail variations that the same content could rank for.
Long-tail keywords have lower volume and less competition but are often more specific and relevant. These queries aggregate into substantial traffic when captured together.

Use keyword research tools to find semantic clusters. Group related terms that share search intent and could be satisfied by a single comprehensive resource.
Total the volume across all variations. This sum represents your maximum addressable search demand.
Click-Through Rate by Position
Not every search generates a click. Not every position receives equal attention.
CTR varies dramatically based on ranking position, query intent, and SERP features present.
Position one typically captures 25-30% of available clicks. Position two drops to 12-15%. By position ten, you’re lucky to see 2% CTR.
Featured snippets, video carousels, and people also ask boxes reduce organic CTR further. Some queries now show AI Overviews that answer questions without requiring clicks.
Estimate realistic CTR for your target ranking position. Conservative estimates prevent disappointment and guide accurate ROI calculations.
Ranking Probability Assessment
Your likelihood of reaching specific positions depends on domain authority, content quality, backlink profile, and competitive intensity.
New sites rarely crack top three positions for competitive terms. Established domains with strong topical authority have significant advantages.
Assess your current domain rating relative to ranking competitors. Calculate the authority gap between your site and pages occupying positions one through five.
If competitors have domain ratings 30 points higher than yours, reaching position one becomes unrealistic in the short term. Focus on more achievable rankings or build authority first.
Conversion Potential and Business Value
Traffic means nothing without conversions. High-potential keywords attract visitors ready to take action.
Evaluate search intent carefully. Informational queries generate traffic but rarely convert immediately. Commercial and transactional queries bring ready-to-buy visitors.
Calculate potential revenue per visitor based on your conversion rate and average order value. Multiply by traffic potential to estimate total keyword value.
A keyword delivering 500 monthly visitors with 5% conversion rate and £100 average value generates £2,500 monthly revenue. That context matters more than raw traffic numbers.
How to Calculate Traffic Potential Step-by-Step
Building accurate traffic forecasts requires systematic analysis. Follow this framework for reliable estimates.
Step 1: Gather Baseline Search Data
Identify your target keyword and variants. Use keyword research platforms to collect monthly search volume for the primary term and related queries.
Export this data to a spreadsheet. Include columns for keyword, search volume, difficulty score, and current ranking if applicable.
Sum total search volume across all variations. This number represents maximum monthly search demand for your topic cluster.
Step 2: Map Current SERP Dynamics
Analyse the actual search results page for your target keyword. Document SERP features present: featured snippets, people also ask boxes, video carousels, shopping results, local packs.
Each feature reduces clicks to organic results. Estimate the percentage of clicks these features capture based on their prominence and relevance.
If 40% of the SERP displays features above organic results, reduce your addressable click volume by 40%.
Step 3: Apply Position-Based CTR Estimates
Traffic potential ≈ search volume × realistic CTR by position × your probability of reaching that position. This formula provides your baseline calculation.

Use these conservative CTR estimates by position:
| Position | Typical CTR Range | Conservative Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25-35% | 28% |
| 2-3 | 10-15% | 12% |
| 4-5 | 5-8% | 6% |
| 6-10 | 2-4% | 3% |
Multiply your adjusted search volume by the CTR for your target position. This gives you baseline traffic potential assuming you achieve that ranking.
Step 4: Assess Your Ranking Probability
Compare your domain authority and content quality to current ranking pages. Assign a probability percentage to reaching your target position.
If your domain rating matches competitors and you plan comprehensive content, assign 70% probability. If you’re significantly weaker, reduce to 30-40%.
Multiply your position-based traffic estimate by this probability factor. The result represents realistic expected traffic.
Step 5: Calculate Final Traffic Potential
Sum traffic estimates across all realistic ranking positions. Weight each by your probability of achieving that position.
Example calculation: Target keyword has 10,000 monthly searches. Related variations add 15,000 more. Total addressable demand: 25,000 searches.
SERP features reduce clicks by 30%. Addressable clicks: 17,500.
You estimate 40% probability of position 3 (12% CTR) and 30% probability of position 5 (6% CTR).
Position 3 potential: 17,500 × 0.12 × 0.40 = 840 visits. Position 5 potential: 17,500 × 0.06 × 0.30 = 315 visits.
Total weighted traffic potential: 1,155 monthly visits.
This methodology produces realistic forecasts that guide investment decisions and content prioritisation.
Essential Tools for Traffic Potential Estimation
Accurate analysis requires reliable data sources. These platforms provide the metrics needed for traffic forecasting.
1. Google Analytics and Search Console
Your own traffic data provides the most accurate insights. A steady climb in organic search traffic over time is one of the strongest indicators that your SEO efforts and keyword choices are working.

Google Analytics shows which keywords currently drive traffic, conversion rates by source, and engagement metrics that reveal content effectiveness.
Google Search Console displays impressions, clicks, and average position for every query where you appear in search results. This data reveals opportunities to improve rankings and capture additional traffic.
Export Search Console data monthly. Track ranking movements and correlate position changes with traffic fluctuations to validate your CTR assumptions.
Identify queries where you rank positions 4-10 with high impression volume. These represent quick wins where small ranking improvements unlock substantial traffic gains.
2. Ahrefs Traffic Potential Metric
Ahrefs calculates traffic potential automatically by analysing the top-ranking page for each keyword. The platform estimates total traffic that page receives from all ranking keywords.
This metric reveals the full opportunity rather than single-keyword volume. You see actual traffic the top position captures across hundreds of related queries.
Use Ahrefs to identify keywords where traffic potential significantly exceeds search volume. These terms unlock topic clusters with substantial aggregate demand.
The platform also provides keyword difficulty scores, click metrics per keyword, and SERP overview data. Combined, these inputs support comprehensive potential analysis.
Export traffic potential data for your target keywords. Compare against your domain rating and backlink profile to assess realistic ranking probability.
3. SEMrush Traffic Analytics
SEMrush estimates competitor traffic from organic search. Enter any domain to see monthly traffic estimates, top-performing pages, and ranking keywords driving that traffic.
This competitive intelligence reveals which keywords actually deliver results for sites in your niche. Focus on terms where competitors receive substantial traffic rather than theoretical volume metrics.
The Keyword Magic Tool provides search volume, trend data, keyword difficulty, and related terms. Use it to build comprehensive keyword lists organised by topic clusters.
SEMrush also tracks SERP features for each keyword, helping you estimate click reduction from non-organic elements.
4. Moz Keyword Explorer
Moz Keyword Explorer combines search volume with CTR estimates and difficulty scores. The Priority metric weighs volume, difficulty, and opportunity to suggest which keywords deserve attention.
The platform shows organic CTR estimates for each keyword based on SERP feature analysis. This helps you calculate realistic traffic potential without manual SERP analysis.
Question and related keyword suggestions reveal the full topic cluster around your primary term. Export these lists to identify all rankable variations.
5. SimilarWeb and Competitive Analysis
SimilarWeb provides traffic estimates for any website, including traffic sources breakdown. See how much traffic competitors receive from organic search versus other channels.
This context helps validate your traffic potential calculations. If competitors ranking for your target keywords receive traffic levels consistent with your estimates, your methodology likely works.
Analyse multiple competitors to understand traffic ranges. Top-performing sites might capture significantly more traffic than weaker competitors at similar positions.
6. Google Keyword Planner
Google Keyword Planner provides search volume ranges directly from Google. While designed for paid search, the data informs organic strategies.
Volume estimates tend to be conservative but reliable. Use Keyword Planner as a baseline reference when other tools show conflicting data.
The platform also forecasts impressions, clicks, and cost for paid campaigns. These metrics help estimate organic opportunity by revealing total search demand.
Understanding Keyword Difficulty in Traffic Analysis
Keyword difficulty quantifies ranking challenge. This score influences your traffic potential realisation.
High difficulty doesn’t eliminate opportunity. It extends the timeline and resource investment required.
Difficulty Score Components
Most platforms calculate difficulty based on domain authority of ranking pages, backlink counts, content quality signals, and historical ranking stability.
Scores typically range from 0-100. Terms scoring 0-30 are relatively easy for newer sites. Scores 30-60 require established domain authority and quality content. Scores above 60 demand exceptional authority and comprehensive content strategies.
Compare your domain rating to average ratings of top 10 ranking pages. If you’re within 10-15 points, the keyword remains achievable. Gaps exceeding 20 points require significant link building before ranking becomes realistic.
Difficulty vs Opportunity Matrix
The most valuable keywords combine reasonable difficulty with high traffic potential. Plot your keyword targets on a matrix:
| Difficulty Level | Traffic Potential | Priority Action |
|---|---|---|
| Low (0-30) | High | Target immediately |
| Low (0-30) | Medium | Include in content plan |
| Medium (31-60) | High | Prioritise with quality content |
| Medium (31-60) | Low | Consider alternatives |
| High (61+) | Very High | Long-term strategic target |
| High (61+) | Low-Medium | Avoid unless strategic value |
Focus resources on opportunities where difficulty matches your capabilities and traffic potential justifies the investment.
Time-to-Rank Considerations
Difficulty directly correlates with ranking timeline. Low-difficulty keywords might rank within weeks. High-difficulty terms often require 6-12 months of sustained effort.
Factor time-to-rank into traffic potential calculations. A keyword delivering 5,000 monthly visits starting immediately provides more value than one delivering 8,000 visits starting in eight months.
Calculate cumulative traffic over 12 months to compare opportunities fairly. The quicker win often produces better total results despite lower individual monthly potential.
Competitor Traffic Analysis Strategies
Understanding competitor performance reveals realistic benchmarks. Their results validate your traffic potential estimates.
Identifying Direct Competitors
Find sites ranking for your target keywords. These are your true SEO competitors regardless of business model or market position.
Export top 10-20 ranking domains for your keyword list. Analyse their traffic, domain authority, content approach, and backlink profiles.
Focus on competitors with similar domain ratings to yours. Their results represent achievable benchmarks rather than aspirational targets.
Estimating Competitor Traffic from Keywords
Use traffic analysis tools to estimate monthly organic visits each competitor receives. Identify which keywords drive the majority of their traffic.
Often, 20% of keywords generate 80% of traffic. Understanding which terms perform best for competitors guides your content priorities.
Compare estimated traffic against keyword search volumes. This reveals realistic conversion of search volume to actual visitors based on rankings, CTR, and competition.
Gap Analysis for Opportunity Identification
Content gap analysis reveals keywords where competitors rank but you don’t. These represent immediate opportunities with proven traffic potential.
Export competitor keyword lists and compare against your rankings. Identify gaps where you lack content or rank below page one.
Prioritise gaps with high search volume, reasonable difficulty, and commercial intent. Create superior content targeting these overlooked opportunities.
Tracking Competitor Movement Over Time
Monitor competitor rankings monthly. Track when they gain or lose positions and correlate with their content updates or link building.
Ranking volatility indicates opportunity. If multiple competitors fluctuate between positions, the SERP remains competitive but penetrable.
Stable rankings dominated by authoritative sites suggest entrenched competition requiring exceptional resources to displace.
SERP Features and Click Distribution
Featured snippets, people also ask boxes, and video carousels capture clicks before users reach organic results. These features dramatically affect traffic potential.
Zero-Click Search Impact
Many queries now result in zero clicks to any website. Users find answers directly in search results.
Informational queries particularly suffer from zero-click behaviour. Questions like ‘how many ounces in a cup’ or ‘population of France’ display instant answers.
Review your target keywords for zero-click risk. If Google provides direct answers, organic traffic potential drops significantly regardless of ranking.
Focus on queries requiring deeper engagement or multiple steps. These maintain click-through rates closer to traditional levels.
Featured Snippet Opportunities
Featured snippets appear above position one. Capturing this placement dramatically increases CTR beyond typical first-position rates.
Identify keywords where featured snippets appear. Analyse the content format Google extracts: lists, tables, paragraphs, or videos.
Structure your content to match snippet formats. Provide concise, direct answers followed by comprehensive explanations.
Monitor Search Console for queries where you rank positions 2-5. These often represent snippet opportunities where improved formatting could capture the featured position.
Local Pack and Shopping Considerations
Local searches display map results above organic listings. Shopping queries show product carousels from Google Shopping.
If your target keyword triggers these features and you can’t appear in them, reduce traffic potential estimates by 40-60%.
For local queries, optimise Google Business Profile to capture map pack placement. This often delivers more traffic than organic positions 1-3 combined.
Building Traffic Forecasts into Content Strategy
Traffic potential analysis informs which content to create and in what order. Build a prioritised content calendar based on realistic opportunity assessment.
Scoring Framework for Prioritisation
Create a simple scoring system combining traffic potential, difficulty, business value, and time-to-rank. Assign points to each factor based on your priorities.
Example scoring framework:
- Traffic potential: 1-10 points based on estimated monthly visitors
- Difficulty: 10 points for easy keywords, decreasing to 1 for very difficult
- Business value: 1-10 points based on conversion potential and customer value
- Time-to-rank: 10 points for quick wins, decreasing for longer timelines
Total scores for each keyword and rank in descending order. This data-driven approach removes guesswork from content planning.
Balancing Quick Wins and Strategic Targets
Include both achievable short-term keywords and ambitious long-term targets in your strategy. Quick wins generate momentum and validate your approach whilst strategic targets build sustainable competitive advantage.
Allocate 60% of resources to keywords you can rank for within 3-4 months. Dedicate 30% to medium-difficulty terms requiring 6-8 months. Reserve 10% for highly competitive strategic keywords needing 12+ months.
This balance produces consistent traffic growth whilst building toward dominant positions in your core topics.
Topic Cluster Development
Group related keywords into comprehensive topic clusters. Create pillar content targeting high-volume primary keywords and supporting content for long-tail variations.
This structure captures traffic across the entire topic whilst building topical authority that improves rankings for all related terms.
Map your keyword research into clusters before creating content. Ensure each cluster has sufficient traffic potential to justify comprehensive coverage.
Measuring Traffic Performance Against Potential
Track actual results against forecasts. This feedback loop improves estimation accuracy over time.
Setting Realistic Milestones
Establish traffic targets based on your potential calculations and time-to-rank estimates. Set monthly checkpoints to measure progress.
Allow 3-6 months for new content to reach stable rankings. Compare actual traffic at that point against your forecast.
Consistent underperformance indicates overly optimistic estimates or execution issues. Adjust your methodology or content approach accordingly.
Attribution and Multi-Keyword Ranking
Track all keywords each page ranks for, not just the primary target. Content that increases relevance often captures traffic from dozens of related queries.
Compare total page traffic against your aggregate traffic potential across all ranking keywords. This reveals whether your content achieves its full opportunity.
Use Search Console to identify unexpected ranking keywords. These reveal content opportunities you didn’t initially target but can optimise further.
Continuous Optimisation Based on Data
Monitor ranking positions weekly. Small improvements in competitive keywords can unlock significant traffic gains.
If you rank position 4-6, focus on reaching positions 1-3. The CTR increase from that movement often doubles or triples traffic from the same keyword.
Update content quarterly based on performance data. Add depth to sections where competitors now outrank you. Refresh statistics and examples to maintain relevance.
Common Traffic Potential Mistakes to Avoid
Several analytical errors consistently lead to inaccurate forecasts. Recognise these pitfalls before they derail your strategy.
Ignoring SERP Feature Click Theft
The most common error: using raw search volume without adjusting for SERP features. Featured snippets, people also ask boxes, and instant answers significantly reduce clicks to organic results.
Always analyse actual SERP layout. Estimate click reduction based on feature prominence. Conservative estimates prevent disappointment.
Overestimating Your Ranking Ability
Wishful thinking leads many to assume they’ll capture position one. Reality: most sites rank somewhere between positions 4-15 for competitive terms.
Be honest about your domain authority relative to competitors. Calculate weighted probability across multiple potential positions rather than assuming best-case scenarios.
Neglecting User Intent Alignment
High search volume means nothing if your content mismatches intent. Users seeking product comparisons won’t engage with brand advocacy content.
Analyse current ranking pages. Understand what format and content angle satisfies the query. Match that approach or risk ranking for a keyword that won’t convert.
Focusing Solely on Primary Keywords
Single-keyword analysis misses the aggregate opportunity from ranking for keyword clusters. Comprehensive content captures traffic from dozens of related queries.
Always calculate total potential across semantic variations rather than evaluating keywords in isolation.
Quick Answers to Key Questions
What are the methods of traffic analysis?
Traffic analysis methods combine quantitative metrics with competitive intelligence. Start with search volume research using keyword tools. Layer in SERP analysis to identify click-stealing features. Apply position-based CTR estimates to calculate realistic traffic. Assess ranking difficulty against your domain authority. Finally, analyse competitor traffic to validate estimates. This multi-method approach produces reliable forecasts that account for real-world search behaviour.
What is the purpose of traffic analysis?
Traffic analysis reveals which content opportunities deserve investment and which to avoid. It quantifies realistic visitor potential before you commit resources to creation or optimisation. This data-driven approach prevents wasted effort on low-potential keywords whilst identifying overlooked opportunities with substantial aggregate traffic. Effective analysis also establishes performance benchmarks for measuring SEO success and guides strategic decisions about content priorities and resource allocation.
Implementing Your Traffic Analysis Framework
You now have the methodology to evaluate keyword traffic potential accurately. Apply this framework systematically to every content decision.
Start by auditing your existing content. Calculate traffic potential for pages already published. Identify underperformers where actual traffic falls short of potential. These represent optimisation opportunities requiring content updates or improved rankings.
Next, analyse your keyword targets. Score each opportunity using traffic potential, difficulty, and business value. Build a prioritised content calendar that balances quick wins with strategic long-term targets.
Remember: SEO is about improving both the quality and quantity of traffic from search engines. Traffic potential analysis ensures you pursue opportunities that deliver both.
Set quarterly reviews to compare forecasts against results. Adjust your estimation methodology based on actual performance. Over time, your traffic predictions will become increasingly accurate, giving you confidence in content investment decisions.
The difference between successful and struggling content strategies often comes down to target selection. Increasing website traffic requires pursuing keywords where you can realistically rank and capture substantial visitors. Traffic potential analysis makes that selection process systematic rather than speculative.
Focus on opportunities where your capabilities match keyword requirements. Build domain authority through strategic content. Track progress against realistic benchmarks. This disciplined approach transforms keyword research from guesswork into a reliable growth engine.